When designing a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system, one of the most critical steps is the heat load calculation. This process determines the amount of heating or cooling required to maintain a comfortable indoor environment, ensuring that the system is both efficient and effective.
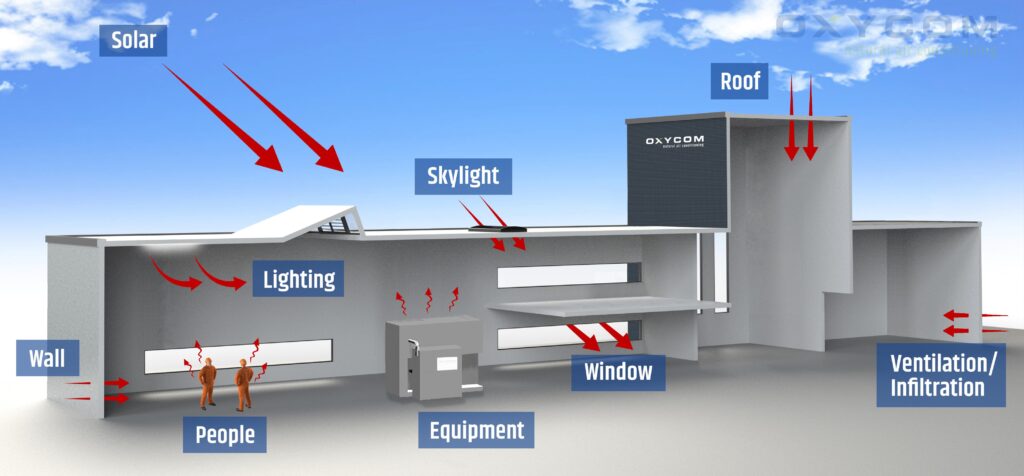
Heat load calculation is a critical process in designing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. It involves determining the amount of heating or cooling needed to maintain a comfortable temperature within a space. Whether you’re cooling a commercial building, a residential home, or an industrial facility, accurate heat load calculations are essential to ensure efficiency, comfort, and cost-effectiveness.
Heat load calculation works by assessing the total heat gain or loss in a given space. This calculation considers various factors that influence temperature, such as:
By analyzing these factors, HVAC engineers can determine the appropriate size and capacity of the heating or cooling system required to maintain a consistent and comfortable environment.
Building Envelope: This includes walls, roofs, windows, and doors, all of which influence heat transfer. Insulating materials, window glazing, and construction techniques are essential considerations in reducing heat gain or loss.
HVAC System Capacity: Based on the calculated heat load, the HVAC system’s size and capacity are selected to ensure it can handle the heating or cooling demands without overworking or underperforming.
Ventilation and Air Distribution: Proper ventilation design ensures that fresh air is adequately circulated, and conditioned air is evenly distributed throughout the space, contributing to overall comfort and indoor air quality.
Energy Efficiency: Modern heat load designs focus on energy efficiency to minimize operational costs and environmental impact. This includes selecting energy-efficient equipment, optimizing insulation, and using smart controls to regulate temperature.
Conclusion
Heat load calculation is a fundamental aspect of HVAC design, ensuring that systems are appropriately sized and capable of maintaining the desired indoor climate. By understanding and implementing accurate heat load calculations, engineers can design systems that offer optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and cost savings, making it an essential process for any building project.